One of many predominant guarantees of marijuana legalization is that the reform may also help curb the illicit market by offering adults with lawful entry to retailers the place merchandise are examined and IDs are checked. However not all states have had the identical expertise in fulfilling that promise—and a brand new report means that native opt-out insurance policies are key elements.
Leafly and Whitney Economics teamed as much as analyze the connection between opt-out legal guidelines and unregulated gross sales. The report, launched on Thursday, discovered that states the place hashish retailers are extra extensively out there—with out as many jurisdictional gaps—have proved far more practical at stamping out the illicit market.
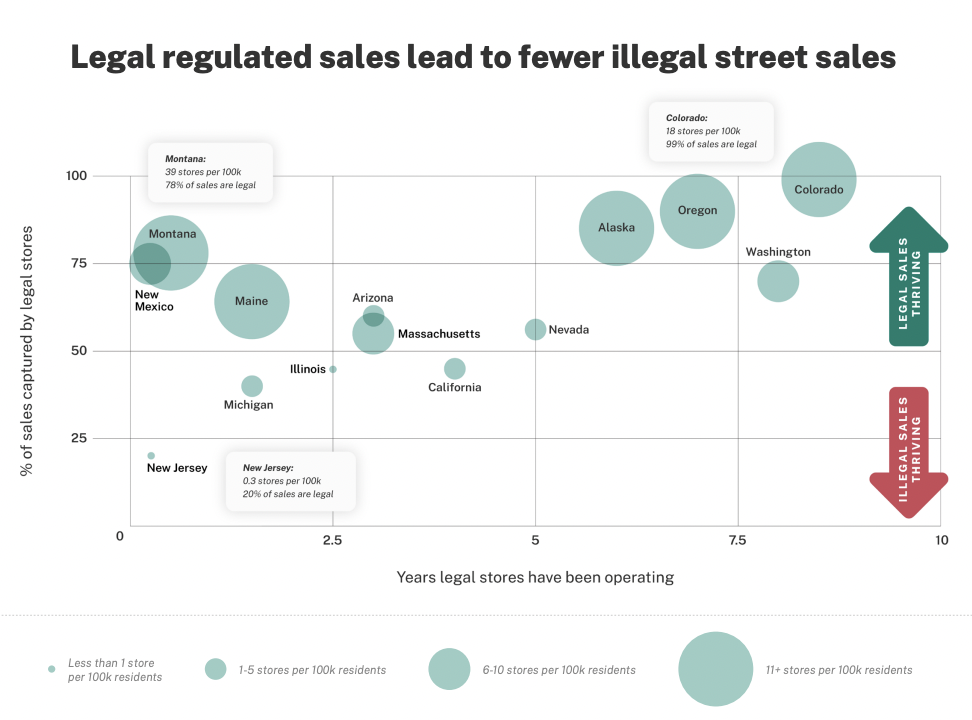
For instance, states the place there are 20-40 marijuana dispensaries per 100,000 residents have seen the best success at competing towards illicit sellers, with 80-90 % of adults reporting that they buy their hashish from regulated storefronts.
By way of Leafly/Whitney Economics.
In distinction, states the place there are fewer than 10 dispensaries per 100,000 residents tends to proceed to see a thriving illicit market, the place round 30-50 % of gross sales occur within the authorized market, the report discovered.
Colorado, Oregon and Alaska stand out as examples of early-adopter states that carried out insurance policies that enabled licensed marijuana retailers to turn out to be extensively accessible to grownup customers.
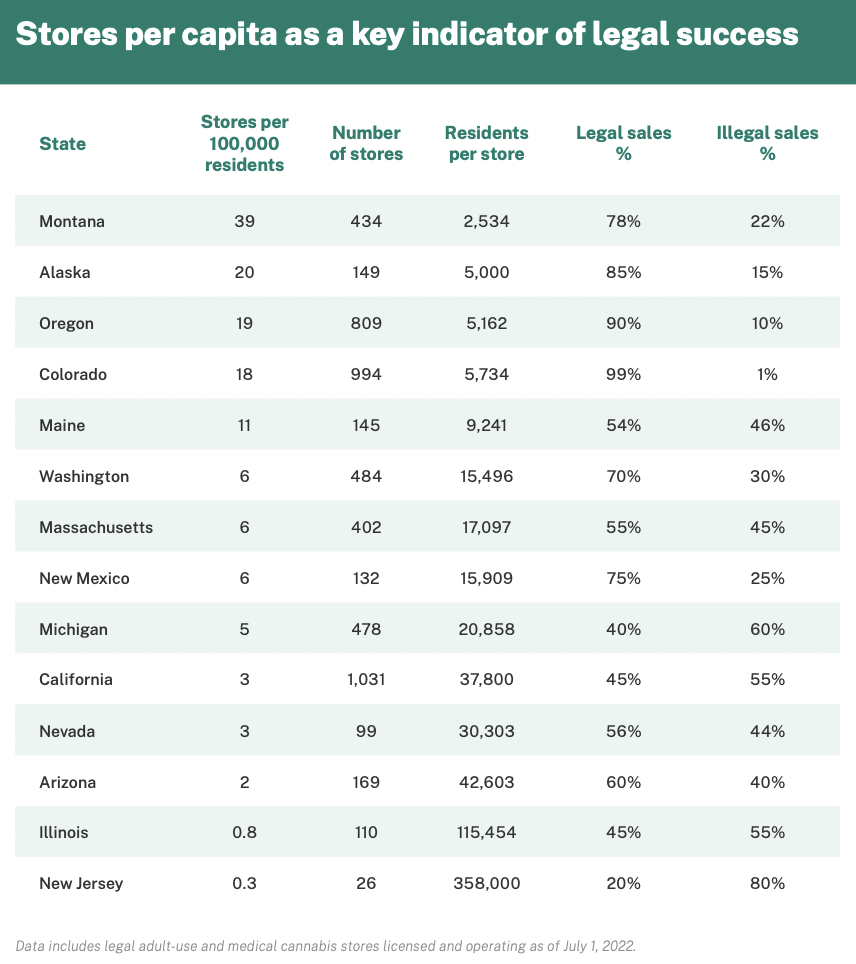
Colorado had 18 marijuana shops per 100,000 individuals on the time of the evaluation in July, and nearly all leisure hashish gross sales (99 %) happen at licensed retailers. In Oregon, there are 19 retailers per 100,000 residents, and the state additionally appears most of its gross sales (75 %) occur throughout the regulated market.
By way of Leafly/Whitney Economics.
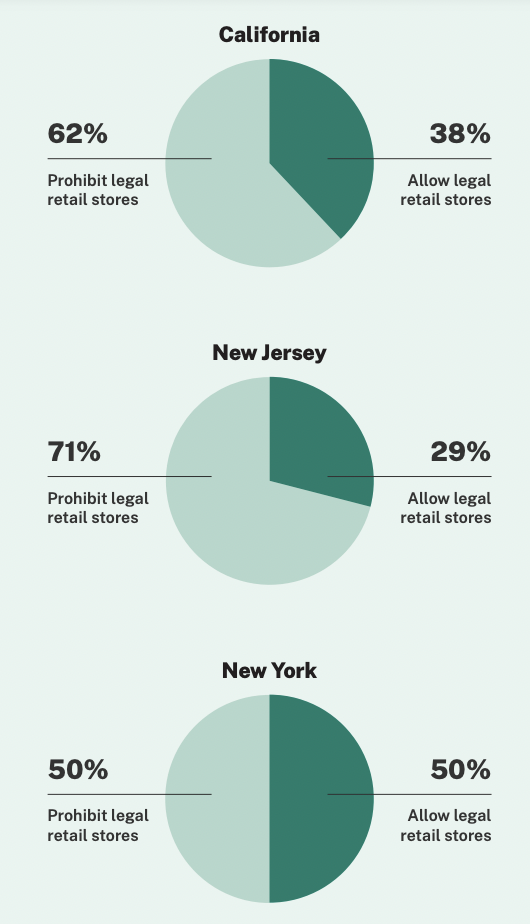
However different states like California—the place native governments are capable of opt-out of permitting most hashish license varieties of their jurisdictions—have been much less efficient at mitigating the illicit market.
Whereas an individual 21 and older can simply discover a plethora of California dispensaries in main cities like Los Angeles and San Francisco, greater than half of the state’s cities and counties have banned all license varieties, making a coverage vacuum that’s empowered illicit sellers to proceed servicing customers exterior of the regulatory framework.
California hashish regulators have tried to attract consideration to the issue, with officers releasing an interactive map earlier this 12 months that reveals precisely the place marijuana companies are being domestically banned. Gov. Gavin Newsom (D) signed a invoice this week that’s partly meant to handle the issue by stopping localities from prohibiting medical hashish supply companies—however the subject is extra systemic.
With simply three marijuana retailers per 100,000 residents within the Golden State, the authorized market captures solely 45 % of hashish gross sales, whereas the remaining 55 % continues to go to the illicit commerce, the brand new report reveals.
“This report demonstrates that authorized, regulated hashish shops put illicit marijuana sellers out of enterprise,” Bruce Barcott, Leafly’s senior editor and the lead writer of the report, mentioned in a press launch.
“Fears surrounding native hashish shops might immediate elected officers to ban hashish firms of their cities,” he mentioned. “However adults in each neighborhood already buy and revel in hashish, authorized or not. The cities and counties that skip out on hashish are basically voting to maintain their native unlawful marijuana markets in enterprise.”
New York regulators are at present accepting functions for the primary adult-use retailers within the state, and the state may quickly function one other instance of how native opt-out insurance policies affect market tendencies. Whereas a big fraction of New York municipalities opted in to allow hashish companies, a whole bunch of cities elected to decide out forward of a deadline early this 12 months.
The lesson from the report is that these opt-out areas will doubtless proceed to see individuals buying marijuana—however the incentive to shift to the regulated market can be tempered by the shortage of conveniently positioned licensed entry.
In New Jersey—the place the leisure marijuana gross sales opened in April and the place a majority of cities initially selected to not allow retailers following the reform implementation—there have been 0.3 dispensaries per 100,000 individuals as of July. Accordingly, the illicit market has maintained dominance over hashish gross sales, accounting for 80 % of purchases.
By way of Leafly/Whitney Economics.
One other issue that’s doubtless hindering efforts to eradicate illicit gross sales is excessive state and native tax charges for merchandise bought in regulated retailers. Analysts and stakeholders have lengthy maintained that imposing extra taxes on marijuana will deter individuals from making the transition to a authorized market, and they also’ve urged lawmakers to take that into consideration when crafting legalization coverage.
“Entry and taxes, these are the keys to buyer migration to the authorized market,” Beau Whitney, founding father of Whitney Economics and a co-author of the report, mentioned. “And proper now we’re seeing unlawful hashish gross sales propped up by opt-out cities and counties.”
The brand new report is predicated on an evaluation that checked out public licensing knowledge from state marijuana regulatory businesses and inhabitants info from the 2020 U.S. Census. The share of hashish gross sales from illicit versus authorized sources was calculated “by evaluating every authorized state’s annual hashish gross sales with that state’s Whole Market Estimation (TME),” the studies methodology part says.
Not solely do native opt-out selections stand to profit illicit marijuana sellers, however the report additionally discovered that areas that block regulated hashish companies usually tend to see public well being points associated to untested merchandise, miss out on job creation alternatives and lose income from native tax choices.
“Authorized hashish regulation works. It places unlawful marijuana sellers out of enterprise and offers minors fewer alternatives to entry weed. It protects public well being by retaining tainted merchandise out of circulation,” the report concludes. “It permits law-abiding adults to abide to abide by the legislation, whereas creating native jobs and tax income. Opting in: It’s the proper factor to do.”
A n earlier 2020 report commissioned by the California Hispanic Chambers of Commerce and Weedmaps equally discovered that native bans on marijuana companies in California have helped the illicit market thrive and disadvantaged the state and municipalities of tax income which have been made all of the extra pressing so as to offset financial losses brought on by the coronavirus pandemic.

